Fuel line size plays a key role in keeping your vehicle or machinery running smoothly. Choosing the right size ensures safe and efficient engine performance. In this article, we’ll explain how the right fuel line affects your engine, explore the trade-offs, and provide a helpful size chart to guide your decision.
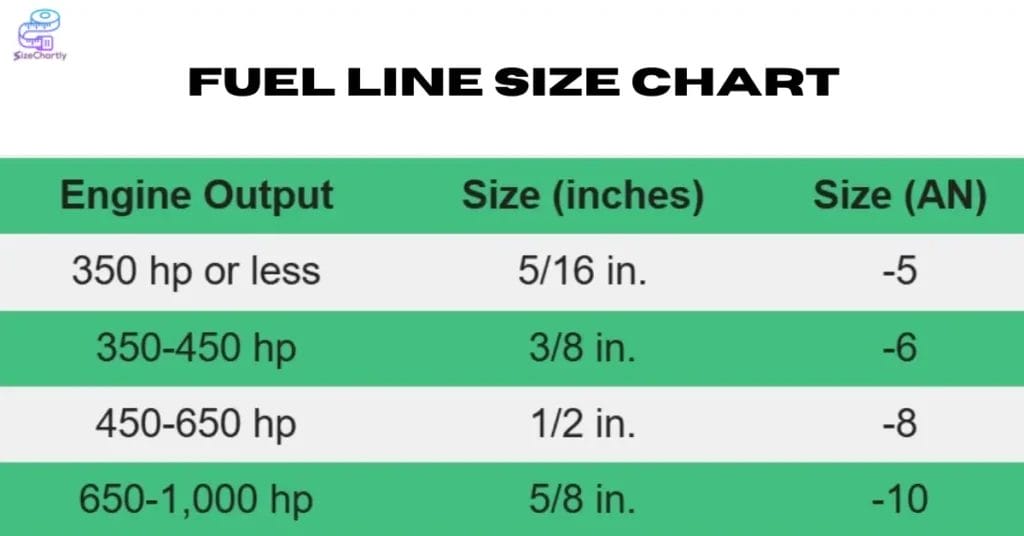
Fuel Line Size Chart
| Recommended Fuel Line Size (from the tank to the pump) | ||
| Engine Output | Size (inches) | Size (AN) |
| 350 hp or less | 5/16 in. | -5 |
| 350-450 hp | 3/8 in. | -6 |
| 450-650 hp | 1/2 in. | -8 |
| 650-1,000 hp | 5/8 in. | -10 |
What Is a Fuel Line?
A fuel line is a pipe that carries fuel from the tank to the engine. It is crucial for ensuring the engine gets the right amount of fuel to run efficiently. However, selecting the right fuel line size involves balancing factors like engine power and fuel type. If the line is too small, fuel flow may be restricted, causing poor engine performance.
On the other hand, a line that is too large may lead to unnecessary fuel consumption. Therefore, it’s important to carefully consider these trade-offs when choosing the proper fuel line size.
Why Fuel Line Size Matters
Choosing the correct fuel line size is essential for maintaining optimal fuel flow and engine performance. When the fuel line is the right size, it ensures that the engine receives the appropriate amount of fuel, preventing poor performance or engine misfires.
However, if the line is too small, fuel flow can be restricted, leading to potential engine damage or inefficiency. On the other hand, a line that is too large may waste fuel and reduce overall performance. Thus, balancing these factors is key. By carefully selecting the right size, you can avoid these issues and improve the overall efficiency of your vehicle or machinery.

Factors Affecting Fuel Line Size
Several factors affect the proper size of a fuel line, including engine power, the type of fuel used, and the specific requirements of the vehicle or machinery. For instance, high-power engines demand larger fuel lines to ensure sufficient fuel flow, while smaller engines may function well with narrower lines.
Additionally, the type of fuel—whether gasoline or diesel—can also impact the size, as diesel engines typically require larger lines for better fuel delivery. Moreover, each vehicle or machine has its own specifications, which must be considered to avoid over- or under-sizing the fuel line.
Balancing these factors is crucial, as selecting the wrong size can lead to inefficient performance, increased fuel consumption, or potential engine damage. Therefore, understanding these variables is key when consulting the Fuel Line Size Chart.
Understanding Fuel Line Diameter
The diameter of the fuel line directly influences the volume of fuel that can flow through it. Larger diameters allow for higher fuel flow, which is ideal for high-performance or larger engines that require more fuel to operate efficiently.
On the other hand, smaller diameters are better suited for fuel-efficient systems, where minimizing fuel consumption is a priority. However, choosing a larger diameter than necessary can lead to excessive fuel use, while selecting a diameter that is too small may restrict fuel flow and cause engine performance issues.
Therefore, it’s essential to carefully balance these factors when deciding on the appropriate size, as the right diameter ensures optimal fuel efficiency and engine performance. Understanding this balance is critical when consulting the Fuel Line Size Chart.
Common Fuel Line Sizes and Applications
Fuel lines come in various sizes, each designed for specific applications. Choosing the right size depends on factors such as engine power, fuel type, and vehicle requirements. For example, smaller fuel lines, such as 5/16 inches, are commonly used in vehicles with lower horsepower or smaller engines, offering fuel efficiency while still providing enough flow for these systems.
On the other hand, larger fuel lines, like 3/8 inches or 1/2 inches, are better suited for higher horsepower engines that require more fuel to operate efficiently. However, opting for a larger size than necessary can lead to wasted fuel and reduced overall efficiency.
Balancing these factors is crucial when selecting the proper fuel line size, as it impacts engine performance, fuel consumption, and long-term reliability. The following chart outlines common fuel line sizes and their typical applications to guide your decision-making.
How to Measure Fuel Line Diameter
To accurately measure the fuel line diameter, you’ll need a caliper or ruler. Start by measuring the inside diameter of the fuel line, as this determines the volume of fuel that can flow through it. Use a caliper for precise measurement, ensuring you measure across the widest part of the line.
If you’re using a ruler, be sure to measure from edge to edge, ensuring it’s straight and aligned. It’s important to match the measured diameter with the appropriate size on the Fuel Line Size Chart to ensure optimal fuel flow and engine performance.
While it may seem simple, any discrepancies in measurement can result in issues like restricted fuel flow or inefficient performance, especially if the wrong size is chosen. Therefore, accuracy is essential in selecting the right size and balancing engine needs with fuel efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Fuel Line Size for Your Vehicle
When selecting the correct fuel line size for your vehicle or machinery, start by considering engine horsepower, fuel type, and other specifications. For instance, high-horsepower engines often require larger fuel lines to meet their higher fuel demands, while smaller engines can function well with narrower lines.
Additionally, the type of fuel—whether gasoline or diesel—affects the choice, as diesel engines generally need larger lines for optimal fuel delivery. Beyond these factors, it’s also important to review manufacturer recommendations and specifications to ensure compatibility with your vehicle. While choosing a larger size may seem like it offers more fuel flow, it can lead to increased fuel consumption and inefficiency.
On the other hand, opting for a smaller line might restrict fuel flow and cause performance issues. Therefore, balancing these trade-offs is crucial when deciding the right size, ensuring both fuel efficiency and engine performance are optimized. Use the Fuel Line Size Chart as a guide to match these factors correctly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Fuel Line Size
One of the most common mistakes people make when selecting fuel lines is choosing a size that is either too small or too large for their engine’s needs. Opting for a smaller line can restrict fuel flow, causing engine misfires or poor performance, especially in high-power engines.
Conversely, selecting a larger line may seem like a way to ensure sufficient fuel flow, but it can lead to unnecessary fuel consumption and decreased efficiency. Additionally, some may overlook the impact of fuel type or vehicle specifications, which can affect the optimal size.
Therefore, it’s crucial to carefully balance these factors and avoid common pitfalls when choosing the right fuel line. By referring to the Fuel Line Size Chart, you can make a well-informed decision that supports both engine performance and fuel efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct fuel line size may seem like a small detail, but it significantly impacts your engine’s performance and lifespan. By selecting the right size, you ensure optimal fuel flow, prevent potential issues, and improve efficiency. Balancing all factors carefully is essential when using the Fuel Line Size Chart.
FAQs
What happens if I choose the wrong fuel line size?
If you choose the wrong fuel line size, you risk either restricting fuel flow or wasting fuel. A line that’s too small may cause fuel starvation, leading to engine misfires or poor performance. A line that’s too large can increase fuel consumption and reduce efficiency.
How do I know which fuel line size is right for my engine?
To determine the correct fuel line size, consider factors like engine horsepower, fuel type, and the manufacturer’s specifications. Higher horsepower engines typically require larger fuel lines, while smaller engines perform well with narrower lines. Use the Fuel Line Size Chart as a guide to match these factors.
Can I use the same fuel line size for all vehicles and machinery?
No, each vehicle or machine has unique requirements based on engine power, fuel type, and other specifications. Using the correct size ensures optimal fuel flow and engine performance. Always consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and refer to the Fuel Line Size Chart for the best match.