Knowing bearing numbers and sizes is crucial for choosing the right bearings. These details allow you to assess load capacity and environmental factors, ensuring you make informed choices that optimize performance and extend durability.
Bearing Number And Size Chart
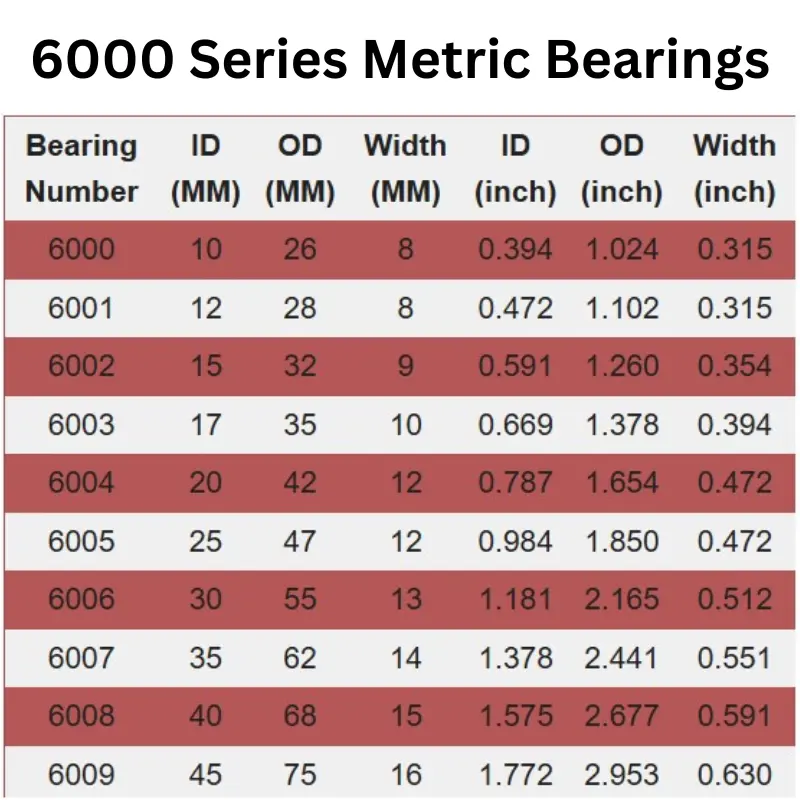
6000 Series Metric Bearings
| Bearing Number | ID (MM) | OD (MM) | Width (MM) | ID (inch) | OD (inch) | Width (inch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6000 | 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.394 | 1.024 | 0.315 |
| 6001 | 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.472 | 1.102 | 0.315 |
| 6002 | 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.591 | 1.260 | 0.354 |
| 6003 | 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.669 | 1.378 | 0.394 |
| 6004 | 20 | 42 | 12 | 0.787 | 1.654 | 0.472 |
| 6005 | 25 | 47 | 12 | 0.984 | 1.850 | 0.472 |
| 6006 | 30 | 55 | 13 | 1.181 | 2.165 | 0.512 |
| 6007 | 35 | 62 | 14 | 1.378 | 2.441 | 0.551 |
| 6008 | 40 | 68 | 15 | 1.575 | 2.677 | 0.591 |
| 6009 | 45 | 75 | 16 | 1.772 | 2.953 | 0.630 |
| 6010 | 50 | 80 | 16 | 1.969 | 3.150 | 0.630 |
| 6011 | 55 | 90 | 18 | 2.165 | 3.543 | 0.709 |
| 6012 | 60 | 95 | 18 | 2.362 | 3.740 | 0.709 |
| 6013 | 65 | 100 | 18 | 2.559 | 3.937 | 0.709 |
| 6014 | 70 | 110 | 20 | 2.756 | 4.331 | 0.787 |
| 6015 | 75 | 115 | 20 | 2.953 | 4.528 | 0.787 |
| 6016 | 80 | 125 | 22 | 3.150 | 4.921 | 0.866 |
| 6017 | 85 | 130 | 22 | 3.346 | 5.118 | 0.866 |
| 6018 | 90 | 140 | 24 | 3.543 | 5.512 | 0.945 |
| 6019 | 95 | 145 | 24 | 3.740 | 5.709 | 0.945 |
| 6020 | 100 | 150 | 24 | 3.937 | 5.906 | 0.945 |
| 6021 | 105 | 160 | 26 | 4.134 | 6.299 | 1.024 |
| 6022 | 110 | 170 | 28 | 4.331 | 6.693 | 1.102 |
| 6024 | 120 | 180 | 28 | 4.724 | 7.087 | 1.102 |
| 6026 | 130 | 200 | 33 | 5.118 | 7.874 | 1.299 |
| 6028 | 140 | 210 | 33 | 5.512 | 8.268 | 1.299 |
| 6030 | 150 | 225 | 35 | 5.906 | 8.858 | 1.378 |
6200 Series Metric Bearings
| Bearing Number | ID (MM) | OD (MM) | Width (MM) | ID (inch) | OD (inch) | Width (inch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6200 | 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.394 | 1.181 | 0.354 |
| 6201 | 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.472 | 1.260 | 0.394 |
| 6202 | 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.591 | 1.378 | 0.433 |
| 6202-10 | 15.875 | 35 | 11 | 0.625 | 1.378 | 0.433 |
| 6203 | 17 | 40 | 12 | 0.669 | 1.575 | 0.472 |
| 6204 | 20 | 47 | 14 | 0.787 | 1.850 | 0.551 |
| 6205 | 25 | 52 | 15 | 0.984 | 2.047 | 0.591 |
| 6206 | 30 | 62 | 16 | 1.181 | 2.441 | 0.630 |
| 6207 | 35 | 72 | 17 | 1.378 | 2.835 | 0.669 |
| 6208 | 40 | 80 | 18 | 1.575 | 3.150 | 0.709 |
| 6209 | 45 | 85 | 19 | 1.772 | 3.346 | 0.748 |
| 6210 | 50 | 90 | 20 | 1.969 | 3.543 | 0.787 |
| 6211 | 55 | 100 | 21 | 2.165 | 3.937 | 0.827 |
| 6212 | 60 | 110 | 22 | 2.362 | 4.331 | 0.866 |
| 6213 | 65 | 120 | 23 | 2.559 | 4.724 | 0.906 |
| 6214 | 70 | 125 | 24 | 2.756 | 4.921 | 0.945 |
| 6215 | 75 | 130 | 25 | 2.953 | 5.118 | 0.984 |
| 6216 | 80 | 140 | 26 | 3.150 | 5.512 | 1.024 |
| 6217 | 85 | 150 | 28 | 3.346 | 5.906 | 1.102 |
| 6218 | 90 | 160 | 30 | 3.543 | 6.299 | 1.181 |
| 6219 | 95 | 170 | 32 | 3.740 | 6.693 | 1.260 |
| 6220 | 100 | 180 | 34 | 3.937 | 7.087 | 1.339 |
| 6221 | 105 | 190 | 36 | 4.134 | 7.480 | 1.417 |
| 6222 | 110 | 200 | 38 | 4.331 | 7.874 | 1.496 |
| 6224 | 120 | 215 | 40 | 4.724 | 8.465 | 1.575 |
| 6226 | 130 | 230 | 40 | 5.118 | 9.055 | 1.575 |
| 6228 | 140 | 250 | 42 | 5.512 | 9.843 | 1.654 |
| 6230 | 150 | 270 | 45 | 5.906 | 10.630 | 1.772 |
6300 Series Metric Bearings
| Bearing Number | ID (MM) | OD (MM) | Width (MM) | ID (inch) | OD (inch) | Width (inch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6300 | 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.394 | 1.378 | 0.433 |
| 6301 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 0.472 | 1.457 | 0.472 |
| 6302 | 15 | 42 | 13 | 0.591 | 1.654 | 0.512 |
| 6303 | 17 | 47 | 14 | 0.669 | 1.850 | 0.551 |
| 6304 | 20 | 52 | 15 | 0.787 | 2.047 | 0.591 |
| 6305 | 25 | 62 | 17 | 0.984 | 2.441 | 0.669 |
| 6306 | 30 | 72 | 19 | 1.181 | 2.835 | 0.748 |
| 6307 | 35 | 80 | 21 | 1.378 | 3.150 | 0.827 |
| 6308 | 40 | 90 | 23 | 1.575 | 3.543 | 0.906 |
| 6309 | 45 | 100 | 25 | 1.772 | 3.937 | 0.984 |
| 6310 | 50 | 110 | 27 | 1.969 | 4.331 | 1.063 |
| 6311 | 55 | 120 | 29 | 2.165 | 4.724 | 1.142 |
| 6312 | 60 | 130 | 31 | 2.362 | 5.118 | 1.220 |
| 6313 | 65 | 140 | 33 | 2.559 | 5.512 | 1.299 |
| 6314 | 70 | 150 | 35 | 2.756 | 5.906 | 1.378 |
| 6315 | 75 | 160 | 37 | 2.953 | 6.299 | 1.457 |
| 6316 | 80 | 170 | 39 | 3.150 | 6.693 | 1.535 |
| 6317 | 85 | 180 | 41 | 3.346 | 7.087 | 1.614 |
| 6318 | 90 | 190 | 43 | 3.543 | 7.480 | 1.693 |
| 6319 | 95 | 200 | 45 | 3.740 | 7.874 | 1.772 |
| 6320 | 100 | 215 | 47 | 3.937 | 8.465 | 1.850 |
| 6321 | 105 | 225 | 49 | 4.134 | 8.858 | 1.929 |
| 6322 | 110 | 240 | 50 | 4.331 | 9.449 | 1.969 |
| 6324 | 120 | 260 | 55 | 4.724 | 10.236 | 2.165 |
| 6326 | 130 | 280 | 58 | 5.118 | 11.024 | 2.283 |
| 6328 | 140 | 300 | 62 | 5.512 | 11.811 | 2.441 |
| 6330 | 150 | 320 | 65 | 5.906 | 12.598 | 2.559 |
Miniature Size Bearings
| Bearing Number | ID (MM) | OD (MM) | Width (MM) | ID (inch) | OD (inch) | Width (inch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 607 | 7 | 19 | 6 | 0.275 | 0.748 | 0.236 |
| 608 | 8 | 22 | 7 | 0.315 | 0.866 | 0.275 |
| 609 | 9 | 24 | 7 | 0.354 | 0.945 | 0.275 |
| 626 | 6 | 19 | 6 | 0.236 | 0.748 | 0.236 |
| R4A | 6.35 | 19.05 | 7.14 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.281 |
Double Row Bearings
| Bearing Number | ID (MM) | OD (MM) | Width (MM) | ID (inch) | OD (inch) | Width (inch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3202 | 15 | 35 | 15.9 | 0.590 | 1.378 | 0.625 |
| 3206 | 30 | 62 | 23.8 | 1.181 | 2.441 | 0.937 |
| 5202 | 15 | 35 | 15.9 | 0.590 | 1.378 | 0.625 |
| 5206 | 30 | 62 | 23.8 | 1.181 | 2.441 | 0.937 |
| 5303 | 17 | 47 | 22.2 | 0.669 | 1.850 | 0.874 |
Wide Bearings
| Bearing Number | ID (MM) | OD (MM) | Width (MM) | ID (inch) | OD (inch) | Width (inch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W204PP | 20 | 47 | 20.64 | 0.787 | 1.850 | 0.812 |
| W205PP | 25 | 52 | 20.64 | 0.984 | 2.047 | 0.812 |
| W206PP | 30 | 62 | 23.81 | 1.181 | 2.441 | 0.937 |
Self-aligning Bearings
| Part Number | Bearing Number | ID (MM) | OD (MM) | Width (MM) | ID (inch) | OD (inch) | Width (inch) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KTN8 | 2205 | 25 | 52 | 18 | 0.984 | 2.047 | 0.709 |
| TS92 | 2206 | 30 | 62 | 20 | 1.181 | 2.441 | 0.787 |
87000 Series Bearings
| Bearing Number | ID (B) (MM) | OD (D) (MM) | Width (W) (MM) | ID (B) (inch) | OD (D) (inch) | Width (W) (inch) | Outer Width (Wo) (inch) | Center Width (Wi) (inch) |
| 87501 | 12 | 32 | 12.7 | 0.472 | 1.260 | 0.500 | 0.394 | 0.480 |
| 87502 | 15 | 35 | 12.7 | 0.591 | 1.378 | 0.500 | 0.433 | 0.480 |
| 87503 | 17 | 40 | 14.3 | 0.670 | 1.575 | 0.563 | 0.472 | 0.538 |
| 87504 | 20 | 47 | 15.875 | 0.787 | 1.850 | 0.625 | 0.551 | 0.600 |
What are Bearings?
Bearings, essential mechanical components, facilitate rotational or linear movement by minimizing friction among moving parts. This functionality is pivotal in diverse applications, from industrial machinery to automotive systems.
Balancing factors such as load capacity, speed, and environmental conditions poses challenges in bearing selection. Understanding these tradeoffs ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Decisions based on bearing number and size charts impact efficiency and reliability, underscoring the need for informed choices. By delving into these aspects, engineers and users can navigate complexities to achieve seamless operational outcomes across various sectors.
Importance of Bearing Numbers and Size Chart
The bearing number and size chart offer essential insights into the dimensions and capabilities of diverse bearings. This information is pivotal for engineers and users alike, guiding decisions based on factors like load handling, speed requirements, and environmental conditions.
However, navigating these charts involves tradeoffs, such as balancing between compact size and load capacity or selecting bearings optimized for specific operational challenges. Challenges may arise from interpreting complex specifications or integrating bearings into intricate systems effectively.
Each decision impacts performance and reliability, emphasizing the need for careful consideration. By leveraging bearing number and size charts effectively, stakeholders can enhance operational efficiency and durability across a wide range of applications, from precision machinery to heavy-duty industrial equipment.
Components of Bearing Numbers
Bearing numbers comprise alphanumeric codes that specify distinct characteristics crucial for selection and application. These codes typically denote parameters such as bore diameter, outer diameter, width, and specific features like sealing or lubrication types.
Understanding these components is vital for matching bearings to operational requirements, balancing factors such as load capacity versus space constraints or environmental resilience. Challenges may arise from deciphering complex codes or accommodating specific performance demands in varied conditions.
Each alphanumeric code impacts bearing performance and reliability, underscoring the significance of informed decision-making based on accurate bearing number and size chart interpretation.
By mastering these components, engineers can optimize machinery performance, enhance longevity, and mitigate operational risks effectively across diverse industrial and mechanical applications.

Types of Bearings
There are various types of bearings, each designed for different load capacities and operational environments. For instance, ball bearings are ideal for light to moderate loads, while roller bearings handle heavier loads but require more space.
Selecting the right type involves tradeoffs, such as choosing between load capacity and compactness or balancing speed with durability. Challenges include ensuring compatibility with existing machinery and adapting to specific environmental conditions.
Each bearing type’s characteristics significantly impact performance and longevity, making it crucial to consult bearing number and size charts for precise specifications. By understanding these differences, engineers can make informed decisions that enhance efficiency, reliability, and operational success across diverse applications.
Understanding Bearing Size Chart
The bearing size chart helps identify the dimensions and specifications of bearings, making it a crucial tool for selection. By providing detailed information on inner diameter, outer diameter, and width, it assists in matching bearings to specific applications.
However, using the chart involves tradeoffs, such as balancing compact size against load capacity or choosing between standard and specialized bearings for particular conditions. Challenges include interpreting the chart accurately and integrating bearings seamlessly into complex systems.
Each decision affects performance and reliability, highlighting the importance of careful analysis. By understanding and utilizing the bearing size chart effectively, engineers can ensure optimal performance, durability, and efficiency in a wide range of applications.
Common Bearing Size Parameters
Key parameters in a bearing size chart include inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), width, and load ratings. These dimensions determine the bearing’s suitability for specific applications, influencing load capacity and operational fit.
Balancing these factors involves tradeoffs, such as choosing a larger OD for higher load ratings while managing space constraints. Challenges can arise from ensuring accurate measurements and compatibility with existing machinery.
Each parameter impacts performance, reliability, and longevity, emphasizing the need for precise selection. By understanding these common size parameters, engineers can make informed decisions, optimizing machinery efficiency and reducing the risk of operational failures. Consulting the bearing size chart thoroughly ensures the best fit for diverse industrial applications.
How to Read a Bearing Size Chart
Learning to interpret a bearing size chart can simplify the process of selecting the right bearing. Start by identifying key parameters such as inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), and width.
Next, consider the load ratings to ensure the bearing can handle the required operational load. Balancing these factors often involves tradeoffs, like choosing a larger bearing for higher loads while managing space limitations. Challenges may arise from deciphering complex charts or matching specific requirements.
Each choice impacts performance and longevity, making it crucial to understand the chart fully. By mastering chart interpretation, engineers can make informed decisions, optimizing machinery performance and reducing downtime across various applications.
Application Examples
Examples of how bearing size charts are applied in different industries and scenarios include automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. In automotive, selecting the right bearing ensures smooth engine function.
Aerospace applications demand high precision and load capacity, often requiring tradeoffs between weight and durability. Each decision impacts performance and reliability, emphasizing the importance of informed selection.
Conclusion
It is important to understand bearing numbers and sizes in order to select the most appropriate bearing for a given application. Bearing numbers and sizes provide important information about both the inner and outer dimensions of a bearing, as well as the bore and groove sizes and the bearing type. Once you understand bearing numbers and sizes, you can select the best bearing for your specific application.
FAQ
Q1: What is the significance of bearing numbers?
A1: Bearing numbers provide essential information about the bearing’s dimensions and characteristics, such as bore diameter, outer diameter, and width. They help in selecting the right bearing for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility.
Q2: How do I read a bearing size chart?
A2: To read a bearing size chart, identify key parameters like inner diameter (ID), outer diameter (OD), width, and load ratings. These metrics help determine the bearing’s suitability for your application. Understanding these parameters allows you to balance factors like load capacity and space constraints effectively.
Q3: What are the common types of bearings?
A3: Common types of bearings include ball bearings, roller bearings, needle bearings, and thrust bearings. Each type is designed for different load capacities and operational environments, such as high-speed applications, heavy loads, or axial loads.
Q4: Why is it important to consider tradeoffs when selecting bearings?
A4: Selecting the right bearing involves tradeoffs, such as balancing load capacity with size or choosing between standard and specialized bearings for specific conditions. Understanding these tradeoffs helps ensure the bearing meets your operational requirements and performs reliably.
Q5: How does the bearing size chart impact performance and reliability?
A5: The bearing size chart impacts performance and reliability by providing accurate measurements and specifications. Properly interpreting the chart ensures the bearing fits your machinery, handles the required load, and operates efficiently, reducing the risk of failures and downtime.