The equipment grounding conductor size chart is essential for electrical safety. It helps select the right size grounding conductor based on the electrical load, preventing damage and risks. With various wire gauge sizes and current ratings, the chart simplifies the selection process for professionals and DIY enthusiasts, ensuring a safe and efficient electrical system.
Equipment Grounding Conductor Size Chart
| Rating (Amps) | Copper (AWG or kcmil) | Aluminum or Copper-Clad Aluminum (AWG or kcmil) |
|---|---|---|
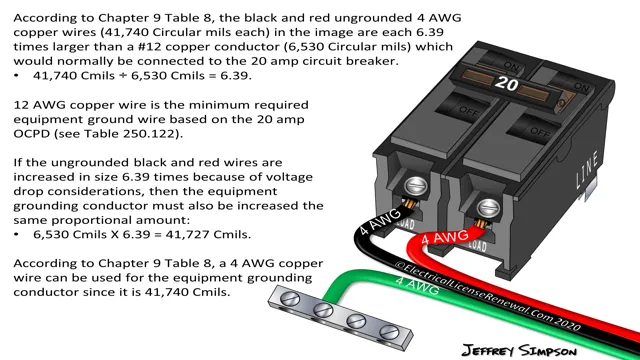
| 15 | 14 | 12 |
| 20 | 12 | 10 |
| 30 | 10 | 8 |
| 40 | 10 | 8 |
| 60 | 10 | 8 |
| 100 | 8 | 6 |
| 200 | 6 | 4 |
| 300 | 4 | 2 |
| 400 | 3 | 1 |
| 500 | 2 | 1/0 |
| 600 | 1 | 2/0 |
| 800 | 1/0 | 3/0 |
| 1000 | 2/0 | 4/0 |
| 1200 | 3/0 | 250 kcmil |
| 1600 | 4/0 | 350 kcmil |
| 2000 | 250 kcmil | 400 kcmil |
What is an Equipment Grounding Conductor?
The equipment grounding conductor, commonly known as the ground wire, is an essential component of all electrical installations. It is a thick, green-colored wire that connects the metallic parts of appliances and electrical devices to the ground terminal of an electrical system. This conductor serves as a safety mechanism to prevent electrocution and equipment damage.
Like a safety net, the equipment grounding conductor catches any excess current that may leak from an appliance and directs it harmlessly into the earth. Think of the ground wire as a way to discharge excess electrical energy that could cause a dangerous situation. Without equipment grounding, any faults in an electrical device or installation could result in electric shocks, fires, and damage to equipment.
Installing an equipment grounding conductor keeps you safe and ensures proper functioning of electrical equipment.
Why is Equipment Grounding Conductor Size Important?
The Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC) is a crucial part of any electrical system. Its primary function is to provide a safe path for electrical faults to flow, thereby protecting people and property from electrocution and fires. The size of the EGC is essential because it determines the path of least resistance for the fault current.
If the EGC is too small, it can overheat and fail, hindering its ability to protect the system. On the other hand, if the EGC is too large, it can be wasteful, increasing the cost of the project. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that the EGC size is appropriate for the electrical system.
By doing so, we can ensure the safety of everyone around the system, as well as the durability and performance of the electrical equipment.
Factors Determining Equipment Grounding Conductor Size
The equipment grounding conductor size chart provides a helpful guide for determining the appropriate size of grounding wire to use for a specific electrical system. However, there are several factors that must be considered when selecting the size of the grounding conductor. The size of the conductor must be appropriate for the maximum fault current that the system can produce, as well as the length of the conductor and the type of insulation used.
Additionally, the temperature rating of the conductor must be considered, as well as the type of environment in which the system will be installed. It’s important to consult with a qualified electrician or electrical engineer to ensure that the equipment grounding conductor is sized appropriately for the specific system and that all relevant safety codes and regulations are followed. By taking these factors into account and using the equipment grounding conductor size chart as a guide, a safe and effective electrical system can be installed and maintained.
Maximum Fault Current
Maximum Fault Current Maximum fault currents can create hazardous conditions, resulting in equipment damage, electrical fires, and electrical shock. Therefore, sizing equipment grounding conductors is critical to ensuring safety and reducing the risk of damage in electrical systems. Several factors determine equipment grounding conductor size, such as the maximum fault current and the required grounding resistance level.
Other factors include the types of materials used in the conduit and conductors, the length of the conductors, and the type of grounding electrode used. Conductors may also need to be upsized to accommodate for short-circuit or fault current peaks, which could exceed the maximum current ratings of the conductors. So, it’s essential to understand these critical factors and to ensure that equipment grounding conductors are adequate for the application as per the National Electric Code (NEC) standards.
Proper grounding protects your equipment and most importantly, protects you and your surroundings from electrical hazards.
Grounding Electrode Conductor Size
The size of the grounding electrode conductor plays a crucial role in the safety and effectiveness of electrical systems. Several factors determine equipment grounding conductor size, including the system voltage, available fault current, and type of grounding electrode used. Generally, the larger the voltage and fault current, the larger the grounding conductor size required.
Additionally, the type of grounding electrode can impact the size of the conductor required. For instance, a rod or pipe electrode may require a smaller conductor than a system grounded with a grounding plate. It is essential to determine the appropriate size of the equipment grounding conductor based on these vital factors to ensure a safe and effective electrical system.
Neglecting to do so can result in electrical shock hazards or equipment failure. Therefore, it’s important to consult with a licensed electrical professional to ensure your electrical system is up to code and properly grounded.
Wire Length and Circuit Load
When it comes to determining the size of the equipment grounding conductor, there are several factors that should be considered. One of these factors is wire length. The longer the wire, the greater the resistance, which in turn can increase the potential for voltage drop.
This is why it’s important to use larger-sized equipment grounding conductors in longer wire runs to help minimize the voltage drop. Another factor to consider is the circuit load. The greater the circuit load, the more heat will be generated, which can cause the conductor to degrade over time.
By ensuring the equipment grounding conductor is sized appropriately for the circuit load, the risk of degradation can be minimized. Overall, taking into account factors such as wire length and circuit load can help ensure the safety and reliability of electrical systems.
Equipment Grounding Conductor Size Chart
If you’re seeking guidance on what size equipment grounding conductor to use for your electrical installation, an equipment grounding conductor size chart can be highly beneficial. This chart helps to ensure that your grounding conductors are sized correctly for your system’s requirements and that your electrical system is safe and reliable. An equipment grounding conductor is an important safety feature that provides a low-impedance path for current to travel in the event of a fault or electrical surge.
To select the correct size of the equipment grounding conductor, you must consider the amperage rating of the circuit, the type of wire used in the circuit, the size of the conductor, and the length of the conductor. The equipment grounding conductor size chart helps you to calculate the correct size for your specific needs, providing peace of mind that your electrical system is correctly grounded and safe.
Table of Conductor Sizes vs. Maximum Load Currents
As an electrician or anyone working with electrical conductors, understanding the proper equipment grounding conductor size is crucial. The equipment grounding conductor size chart provides a clear overview of conductor sizes and their maximum load capacities. The chart is divided into columns, each representing a specific conductor size, and rows, each indicating the maximum load current in amperes.
The chart displays the sizes of copper and aluminum conductors in AWG or American Wire Gauge. The copper conductor options range from 14 AWG to 1000kcmil, while the range for aluminum conductors is from 12 AWG to 1000kcmil. This chart’s purpose is to help professionals understand the limitations of an equipment grounding conductor and determine the correct size for the maximum current allowed.
Using an undersized conductor could result in equipment failure, fire or even electrocution. So, always remember to follow the recommended conductor size, as noted in the equipment grounding conductor size chart, to maintain the highest level of safety for yourself and others.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the equipment grounding conductor size chart may look confusing at first, but it’s simply an organized way to determine the appropriate size needed to provide safety and prevent electrical hazards. So, let’s not get shocked by inadequate grounding and always remember – safety first, watt second!”
FAQs
What is an equipment grounding conductor?
An equipment grounding conductor is a wire that connects non-current-carrying metal parts of equipment to the grounding electrode of a building’s electrical system.
How do I determine the size of an equipment grounding conductor?
The size of an equipment grounding conductor is determined by the ampacity of the circuit it is protecting. You can use an equipment grounding conductor size chart to find the appropriate size.
What is the purpose of an equipment grounding conductor size chart?
An equipment grounding conductor size chart is used to ensure that the wire size of the equipment grounding conductor is appropriate for the ampacity of the circuit it is protecting. This helps to prevent electrical shock and fires.
Can I use a smaller equipment grounding conductor than recommended on the size chart?
No, you should always use the size recommended on the equipment grounding conductor size chart. Using a smaller wire can result in inadequate protection and compromise the safety of the electrical system.